Phoenix Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitor
Glossary
Project-specific Terms
A
- acrometron
- [statistics]
- The measure of the highest predicted value of a rhythm.
- Contrast with bathymetron.
- acrophase
- [statistics]
- 1. Measure of timing of a rhythm in relation to a defined reference time point selected by the investigator (e. g., local midnight for circadian rhythms); used for data which can be described by the fitting of a mathematical model, e.g., a cosine curve, and represents the crest time of the cosine curve best fitting to the data; may be expressed in (negative) degrees as the lag from the acrophase reference (360'C =1 period) or in calendar time units (e.g., hours and minutes for circadian rhythms, days or months for infradian rhythms). (source: AAMCC)
- 2. n. The time at which the peak of a rhythm occurs. Note: Originally, acrophase referred to the phase angle of the peak of a cosine wave fitted to the raw data of a rhythm (time series). When the term is applied to the actual rhythm, the acrophase will likely vary from cycle to cycle. Unit of measurement: hours (h) or degrees of circumference (�) in relation to an absolute or arbitrary reference. Caveat: The official units of time and of plane angle in the International System of Units are, respectively, the second and the radian. // Cf. cosinor and peak. (source: circadian.org)
- 3. The lag between the reference time (midnight, or 0000 hours in a 24-hour day) and the time of the rhythm's crest.
- activity of daily living (ADL)
- [medicine]
- the things a person normally does in daily living including any daily activity performed for self-care (such as feeding, bathing, dressing, grooming), work, homemaking, and leisure
- health professionals routinely refer to the ability or inability to perform ADLs as a measurement of the functional status of a person
- (source: Wikipedia)
- ADL
- [medicine]
- See activity of daily living.
- amplitude (A)
- [statistics]
- 1. Half the total predictable change in a rhythm.
- 2. The measure of one half of the extent of the rhythmic change estimated by the mathematical model (e.g., cosine curve) best fitting to the data (e.g., the difference between the maximum and the rhythm-adjusted mean (MESOR) of the best fitting curve).
- (source: AAMC)
- artery
- [physiology]
- A blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the body.
- Contrast with vein.
B
- bathymetron
- [statistics]
- The measure of the lowest predicted value of a rhythm.
- Contrast with acrometron.
- bathyphase
- 1. The time of the lowest point of a mathematical model (e. g., cosine curve) fitted to a time series and describing a rhythm. If a sine or a cosine curve is fitted, the bathyphase will differ 180' from the acrophase, measured in relation to a defined reference time point selected by the investigator (e.g., local midnight for circadian rhythms); may be expressed in degrees as the lag from the phase reference (360' = I period) or in calendar time units (e. g., hours and minutes for circadian rhythms, days or months for infradian rhythm). (source: AAMCC)
- 2. n. The time at which the trough of a rhythm occurs. Note: This term is very rarely used. Unit of measurement: hours (h) or degrees of circumference (�) in relation to an absolute or arbitrary reference. Caveat: The official units of time and of plane angle in the International System of Units are, respectively, the second and the radian. // Cf. Acrophase. (source: circadian.org)
- biology
- [definition needed]
- biometric, biometrics
- [definition needed]
- blood flow
- [definition needed]
- blood pressure
- [physiology]
- the pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the blood vessels
-
Unless indicated otherwise, blood pressure refers to systemic arterial blood pressure,
i.e., the pressure in the large arteries delivering blood to body parts other than the lungs, such as the brachial artery (in the arm).
The pressure of the blood in other vessels is lower than the arterial pressure.
-
Systemic arterial blood pressure is maintained by:
- The contraction of the left ventricle,
- The resistance of the arterioles and capillaries,
- The elasticity of the arterial walls, as well as
- The viscosity and volume of the blood.
- Blood pressure is expressed as relative to the ambient atmospheric pressure.
Its values are universally stated in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
- See also systolic blood pressure and
diastolic blood pressure.
- (source: Wikipedia)
- blood pressure excess
- See HBI.
- blood pressure mean
- [definition needed]
- body motion
- [definition needed]
C
- capillary
- [physiology]
- One of the tiny blood vessels that connect the arterioles (the smallest divisions of the arteries)
and the venules (the smallest divisions of the veins).
The capillaries form a fine network in many parts of the body.
- CAHRV
- See chronome alterations of heart-rate variability.
- cardiovascular
- [physiology]
- adj. Of or pertaining to or involving the heart and blood vessels.
- Contrast with vascular, a narrower concept that excludes the heart.
- The circulatory system is composed of the heart and blood vessels, and carries nutrients and oxygen to the tissues of the body and removes carbon dioxide and other wastes from them.
- Cardiovascular diseases affect the heart and blood vessels and include arteriosclerosis, coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, arrhythmia, heart failure, hypertension, orthostatic hypotension, shock, endocarditis, diseases of the aorta and its branches, disorders of the peripheral vascular system, and congenital heart disease.
- (source: medterms.com)
- cardiovascular variability
- [definition needed]
- See also vascular variability.
- See also heart rate variability.
- CHAT
- Acronym for circadian hyper-amplitude-tension.
- Acronym for Cetacean Hearing and Telemetry
- chronobiology
- [biology]
-
- That aspect of biology concerned with the timing of biological events, especially repetitive or cyclic phenomena in individual organisms. (source: Stedmans)
- The study of biological systems as affected by time. Aging, biological rhythms, and cyclic phenomena are included. Statistical, computer-aided mathematical procedures are used to describe, in mathematical terminology, various biological functions over time. (source: Online Medical Dictionary)
- The scientific study of the effect of time on living systems. (source: Dorlands)
- A field of science that examines periodic (cyclic) phenomena in living organisms. (source: Wikipedia)
- The science of investigating and objectively quantifying phenomena and mechanisms of the biologic time structure, including the rhythmic manifestations of life. (source: AAMC)
- n. The scientific study of biological rhythms. adj. = chronobiological. (source: circadian.org)
- chronobiometry
- [definition needed]
- chronodesm
- [in progress] A time-qualified reference range.
- chronodesmic band
- [definition needed]
- chronogram
- Display of data as a function of time. (source: AAMC)
- chronome
- 1. The quantitative description of some time-dependent feature. The time-structure of some phenomenon, frequently biologic.
- 2. n. The full complex of rhythms and temporal trends in an organism. The chronome consists of a multi-frequency spectrum of rhythms, trends, and residual structures, including intermodulations within and among physiological variables as well as changes with maturation and aging. // adj. = chronomic.
- (source: circadian.org)
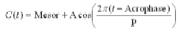 [this equation is obsolete; also, need image with better resolution]
[this equation is obsolete; also, need image with better resolution]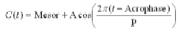 [this equation is obsolete; also, need image with better resolution]
[this equation is obsolete; also, need image with better resolution]